Sustainable Intelligent Ecosystems
AI and data are central to value creation in the digital economy. Business, government, and civil society leaders need to collaborate on trust, sustainability, and inclusion, balancing the speed of innovation with resource consumption and equitable access.
Evolution from 2025
Over the past year, the Sustainable Intelligent Ecosystems theme has moved from experimentation to mainstream adoption. AI now reaches over one billion users worldwide, with competitive advantage shifting from large foundational models to specialized vertical solutions. At the same time, the falling cost of ambient sensors is accelerating their widespread deployment, creating an invisible layer of intelligence.
Yet this rapid growth has exposed a critical paradox: while access to AI tools is expanding, the infrastructure needed to sustain them remains highly unequal. Energy has become a major constraint, with data-center and AI electricity use projected to double by 2030, outpacing clean-energy development. At the same time, disparities in access to computing power, semiconductors, GPUs, and other hardware are widening.
Consequently, current trends have shifted focus from democratizing AI systems to securing the foundational infrastructure and resources that make AI work: renewable energy, sovereign computing capacity, and trusted API-based frameworks for sharing unique datasets.
When it comes to emerging trends, the advances made in the last year in the “Deploying Autonomous Systems at Scale” trend have given rise to two separate axes of progress: the cognitive and physical autonomy of systems. These two dimensions, despite being closely intertwined, are progressing at different speeds each with its own research frontier, industrial ecosystem, and societal implications. Agentic AI is reshaping how digital systems process information and achieve cognitive tasks, while Generalist Robots are redefining how systems interact with, and transform, the physical world.
Sustainable Intelligent Ecosystems: Evolution of Digital Economy Trends Across DET 2024–2026

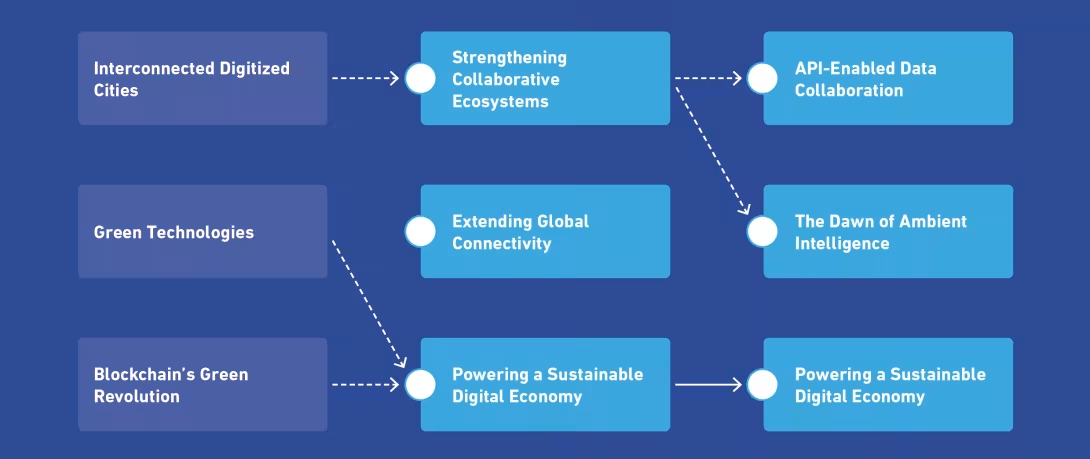
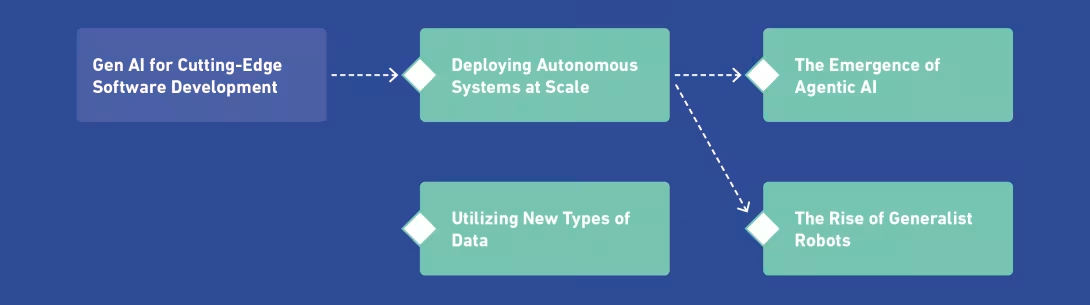

How to build Sustainable Intelligent Ecosystems?
To capitalize on the opportunities presented by the digital economy trends in this theme, stakeholders should collaborate to develop:
Interoperable digital infrastructure
Common standards to integrate intelligent systems securely and efficiently into specific industry workflows.
Trustworthy data governance
robust frameworks on secure data sharing, protecting individual privacy, and defining liability for autonomous systems.
Sustainable resource management
energy-efficient digital infrastructure and circular design to manage the escalating resource demands of AI deployment.
Explore the trends in this theme
THE RISE OF VERTICAL AI
THE RISE OF VERTICAL AI
Current trend
Competitive advantage in AI is shifting from big foundational models to specialized solutions using proprietary data to solve specific problems.
API-ENABLED DATA COLLABORATION
API-ENABLED DATA COLLABORATION
Current trend
APIs create potential for organizations and nations to unlock innovation by sharing data while remaining in control of sensitive information.
THE DAWN OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
THE DAWN OF AMBIENT INTELLIGENCE
Current trend
Sensors in everyday environments are forming an invisible layer of intelligence, using edge computing to optimize decisions and experiences.
POWERING A SUSTAINABLE DIGITAL ECONOMY
POWERING A SUSTAINABLE DIGITAL ECONOMY
Current trend
AI and data centers’ demand for electricity is constraining their potential to scale, making clean energy and efficiency strategic priorities.
THE EMERGENCE OF AGENTIC AI
THE EMERGENCE OF AGENTIC AI
Emerging trend
AI agents can increasingly execute workflows proactively and autonomously, creating potential to make organizations smaller and more efficient.
THE RISE OF GENERALIST ROBOTS
THE RISE OF GENERALIST ROBOTS
Emerging trend
Sophisticated robots that can flexibly perform diverse tasks are becoming cheaper, promising efficiency gains but also disrupting employment.
Read the Digital Economy Trends 2026 report
Explore the full insights and analysis of the 2026 research.