AI Accelerated Workforce Transformation
AI is rapidly reshaping work, displacing jobs while necessitating investment in new skills such as data literacy and digital collaboration.
Total potential economic value creation
US$4.91 trillion
What does this trend encompass?
AI is catalyzing the fastest workforce transformation in history, creating both productivity gains and profound structural pressures on employment. While AI delivers automation and efficiency improvements that make job displacement economically attractive, it also demands new skill sets — such as AI and data literacy and digital collaboration — that require sustained investment in workplace development. This trend builds on 2025's emphasis on developing high-level skills to enhance accessibility to emerging digital technologies, including AI. It calls on organizations to manage workforce transitions strategically, creating opportunities and fostering inclusion rather than widening economic divides through job displacement.
Why is it important?
In 2019, it was projected that over one billion people would need reskilling to avoid skills gaps that hinder inclusive economic growth due to the digital transition. Today, the unfolding of workforce transformation is evident. Implementing proactive upskilling and reskilling programs is essential to ensure that human-digital collaboration in the workplace is effective and that its benefits are shared broadly rather than concentrated among the few.
Enabling conditions and countries’ readiness
According to DET survey respondents, creating a digitally capable and secure workforce depends on:
Digital for Work and Training: workforce upskilling and re-skilling are needed to facilitate a smooth transition toward a hybrid human–machine workforce, minimizing job displacement while promoting a more inclusive and equitable transformation.
Industry Digital Transformation: industry-wide uptake of AI tools in core processes would make task changes and new roles clearer, creating pathways to an AI-complemented work environment that redeploys staff instead of reducing them.

Digital Capabilities: baseline digital and AI literacy, combined with privacy and cybersecurity competence, will drive AI-workforce transformations to raise productivity without widening exclusion.
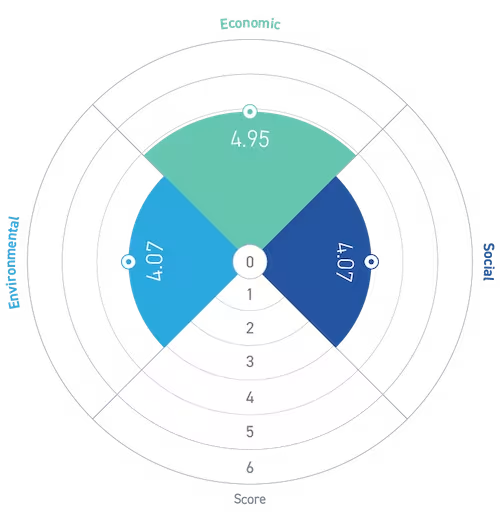
Economic, social, and environmental impact
This trend ranks in the middle-lower range across positive economic (4.95), social (4.07), and environmental (4.07) impacts. This reflects how automation enhances productivity, but slow reskilling and job displacement could limit economic and social outcomes, and high energy use offsets potential sustainability gains.
Recommendations
Private sector
Establish enterprise-wide AI transition programs
that treat reskilling as a strategic investment, co-developing role-specific learning pathways with technology partners and educational institutions.
Adopt skills-based, continuous learning within high impact sectors
such as healthcare and manufacturing with a focus on data, AI, and cybersecurity competencies.
Use verifiable and transferable micro-credentials
that are recognized across the industry (not just within a single company) to validate competencies, expand talent pools, and promote career mobility.
Public sector
Co-create verifiable micro-credential standards
with technology and professional services industries and higher education to validate AI, data, and cybersecurity competencies and enable skills-based hiring.
Establish public-private reskilling funds through tax incentives and matching grants
for employer-led training, providing wage insurance and transition support for displaced workers to ensure market relevance and proactive workforce readiness.
Mandate that public procurement for service contracts recognize verifiable, cross-border micro-credentials
to catalyze market adoption.
Launch market-driven, multi-lingual training hubs
offering short courses, on-the-job learning credits and assessment centers, especially in remote, rural, and low-income communities.
IGOs, IOs, and others
Co-develop shared competency standards for AI and digital workplace skills
with governments, businesses, and educators. Use those standards to create cross-border learning credentials that ensure workers' skills are valued regardless of where they were learned.
Create public e-learning platforms and training hubs
that match job demand with available learning resources. Co-design training with local employers to deliver practical, market-relevant skills that lead to real employment.
Create transparent benchmarking tools and national AI workforce readiness assessments
which track countries' progress toward their stated reskilling targets. Use shared and agreed-upon indicators to generate actionable gap analyses and cross-country assessments.
Support capacity-building for local educators, civil servants, and community business leaders
to help them lead local workforce transformation initiatives in regions facing acute displacement challenges.
Read the Digital Economy Trends 2026 report
Explore the full insights and analysis of the 2026 research.